Hey ChatGPT,
What is AI?
(WEBSITE UNDER CONSTRUCTION)
-

Early Pioneers: A Brief History
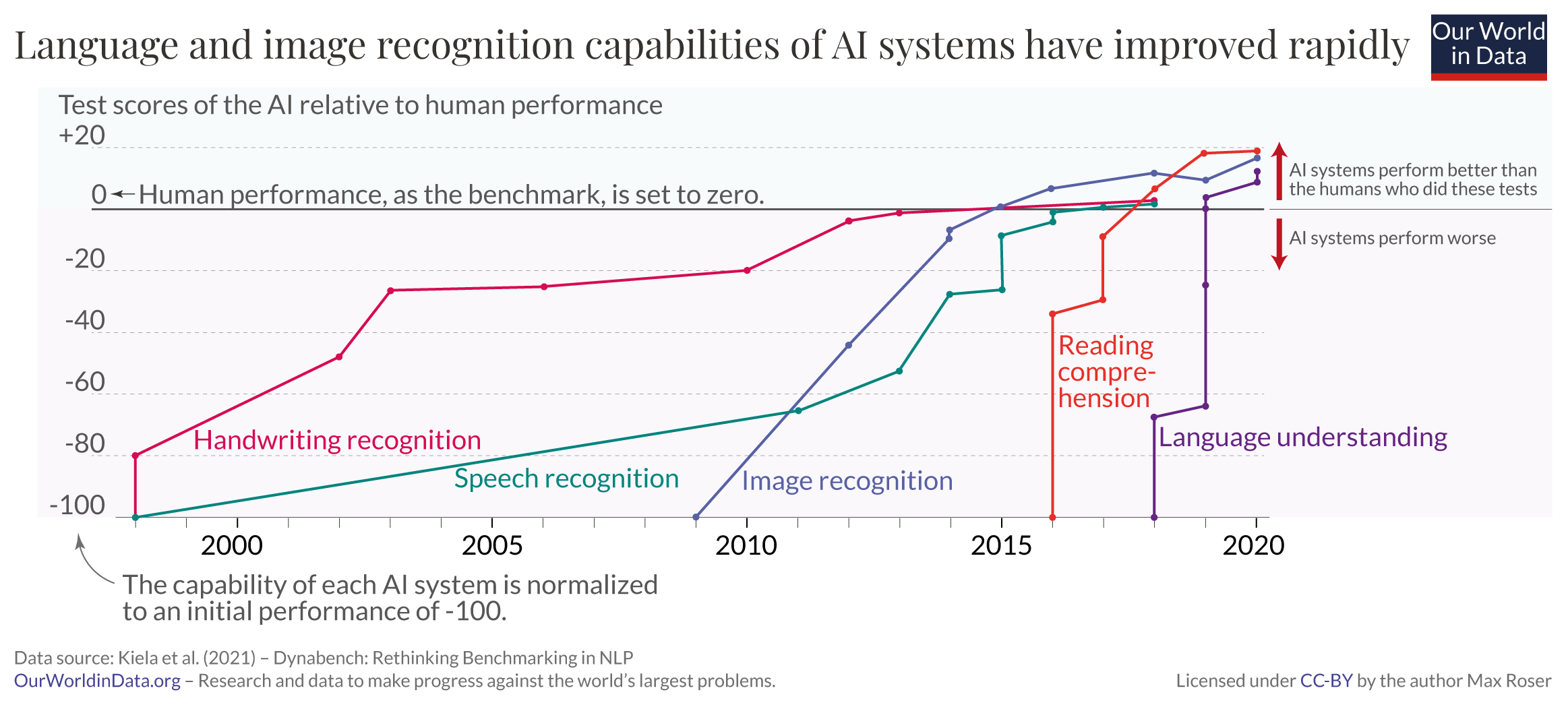
Machine learning has been around since the 1950’s. Explore the timeline.
-

The Basics
Types of machine learning algorithms, with links to additional guides if you want to learn more.
-

Medical Applications
Explore recent advancements or even submit your own that the class may find interesting!
-

Startups to Watch
Companies of interest in this space.
Submit a company if you don’t see it here!
Submit a company or emerging application of interest!
German filmmaker Fritz Lang introduces a humanoid robot who tries to take over a mega-city. As of early 2023, the film is public domain in the US. IMDB
Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer (ENIAC) was built by the United States Army, and in 1946 it was put into service at the University of Pennsylvania.
Research continued but was slow due to lack of computational power.
1945: First Digital Computer
1954: First Machine Translation
1992: Chinook Checkers - Almost Win
2011: IBM Watson Wins Jeopardy!
Marion Tinsley, world champion checkers player, faces off against Jonathan Shaeffer’s Chinook program (University of Alberta). Tinsley withdrew due to health issues and died soon after. For more on this complex interaction of man vs. machine, check out Alexis Madrigal’s summary at the Atlantic, Schaeffer’s blog post here, or Schaeffer’s book, One Jump Ahead. Fun fact: Tinsley lived in Tallahassee, Florida at the time.
1997: Deep Blue Wins Chess
IBM’s Deep Blue defeats famous world champion chess player Garry Kasparov in an official match. (Deep Blue lost that same match in 1996). IBM used a supercomputer with VLSI chips specifically built for this purpose. For more information, check out this IEEE article.
Filmmakers imagine a dystopian artificial intelligence.
IBM and Georgetown researchers develop the first computer translation program, which translated Russian to English on an IBM 701 computer.
1943: Perceptron Invented
Warren McCulloch and Walter Pitts describe a perceptron in their paper "A Logical Calculus of Ideas Imminent in Nervous Activity,” which was first neural network. It uses the concept of a biological neuron to create a binary classifier. However, it couldn’t be tested as the hardware to do it hadn’t been created yet. Frank Rosenblatt built the first implementation at Cornell in 1958.
A BRIEF HISTORY
1927: Metropolis
1951: K-Nearest Neighbor Invented
A supervised learning technique is developed by Evelyn Fix and Joseph Hodges for classification and regression. Read their original paper here.
1952: Checkers
Arthur Samuel at IBM designed first algorithm to play checkers and coined the term “machine learning”. His program was released in 1955, when a single computer would take up an entire room and programs were carried out using paper cards.
1958: Perceptron Implemented
Frank Rosenblatt built the first implementation in 1958 at the Cornell Aeonautical Laboratory built a perceptron machine, funded by the US Navy. It was a physical machine, not a program on a computer. Potentiometers were used to vary the weights between neurons. (source)
Research continued but was slow due to lack of computational power.
1994: Chinook Wins World Championship
The Chinook program wins the Checkers World Championship, the first computer program to do so in a human competition. For image source and more information, click through the image to the University of Alberta.
1967: Nearest Neighbor Algorithm Advances
Thomas Cover at Stanford and his student, Peter Hart, publish their highly influential paper on nearest neighbor methodology for pattern recognition. Read Dr. Cover’s recall of that time here and reference the original paper here. Marcello Pelillo explores the origin of the nearest neighbor concept, dating back to Alhazen in the Islamic golden age, influenced by Ptolemy.
2012: Google Cat Image Recognition
Thanks to the new ubiquity of smartphones with cameras and burgeoning image datasets available on the internet, scientists leverage the plethora of cat and dog images to train for object recognition.
IBM’s Watson computer defeated Jeopardy superstar Ken Jennings in a highly publicized match. Read more about IBM’s approach in their own words here.
THE BASICS
-

Supervised Learning
-

Unsupervised Learning
-

Reinforcement Learning
-

Generative AI